QoE Prediction Using AI/ML Framework in Distributed ORAN Architecture¶
Author: Wafi Hasan
Published: November 8, 2024
In this era of telecommunications where features are being upgraded round the clock, ensuring high user satisfaction is paramount. QoE or Quality of Experience is an important metric that has enabled us to do the above mentioned task. The definition of QoE, which was adopted by ITU in Recommendation ITU-T P.10/G.100 is:
The degree of delight or annoyance of the user of an application or service. It results from the fulfillment of his or her expectations with respect to the utility and / or enjoyment of the application or service in the light of the user’s personality and current state.
This was given by Qualinet of COST (European Cooperation in Science and Technology) Association.
QoE Prediction¶
Quality of Experience (QoE) prediction models have emerged as a tool to achieve this. QoE represents the user’s subjective satisfaction with a network service, and accurately predicting it helps operators enhance service delivery to meet user expectations. By predicting and managing potential issues beforehand, QoE models play a vital role in guaranteeing non-interruptive, high-quality service, even under heavy network load or in dynamic environments.
5G networks are designed to accommodate a wide range of services, from Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC) for mission-critical applications to massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC) for IoT. Predicting QoE in such a complex landscape allows operators to proactively manage network resources, adjusting parameters to ensure that each service meets its unique quality requirements. In this blog, we will dive into how QoE prediction models operate within the 5G framework, their benefits, and various use cases that highlight their potential impact on enhancing user experience.
To have a look at our tutorial of QoE prediction, refer to the video below:
Dynamic Resource Allocation¶
Predicting QoE in real-time enables operators to dynamically allocate network resources to maintain service quality. In scenarios where network demand spikes, QoE prediction helps identify which users or applications require prioritized resources. For example, during a live-streamed sports event, demand may surge, potentially degrading video quality. With QoE prediction models, the network can proactively allocate resources to ensure users experience minimal buffering and optimal video quality, resulting in higher satisfaction. This dynamic allocation improves the network’s efficiency and adaptability, ensuring critical services are maintained during peak usage periods without compromising overall user experience.
Proactive Quality Control¶
QoE prediction also enables proactive quality control by forecasting potential drops in user satisfaction due to network conditions. For instance, in areas prone to poor connectivity, the model can predict when a user’s quality may dip, allowing operators to adjust parameters such as bandwidth allocation or latency management to preemptively counter the issue. In the case of applications sensitive to delays—such as online gaming or video conferencing—these adjustments ensure smooth, uninterrupted sessions, preventing user dissatisfaction. Proactive quality control thus helps maintain a positive user experience by mitigating issues before they impact the end-user, building trust and loyalty in the service.
Enhanced Customer Support and Troubleshooting¶
With QoE prediction models, customer support teams gain a valuable tool for preemptive troubleshooting. By analyzing QoE data and identifying patterns, support teams can detect recurring issues and address them before they escalate into larger problems. If the model predicts that certain users are likely to experience reduced quality due to network congestion, operators can implement measures to alleviate congestion and notify users of any temporary adjustments. This proactive approach not only reduces the volume of user complaints but also improves service transparency, helping users feel more informed and supported.
Support for Network Slicing¶
Network slicing in 5G allows operators to allocate network resources into dedicated “slices” tailored to different use cases. QoE prediction helps optimize these slices by predicting the quality demands of each user or application within a slice. For example, an autonomous vehicle may need a high-priority slice with low latency and high reliability, while a streaming service may prioritize data rate and stability. By predicting the QoE requirements of each slice, operators can dynamically adjust resources to ensure every slice meets its specific QoE targets, enhancing the reliability and effectiveness of network slicing.
Utilizing AI/ML for Prediction Models¶
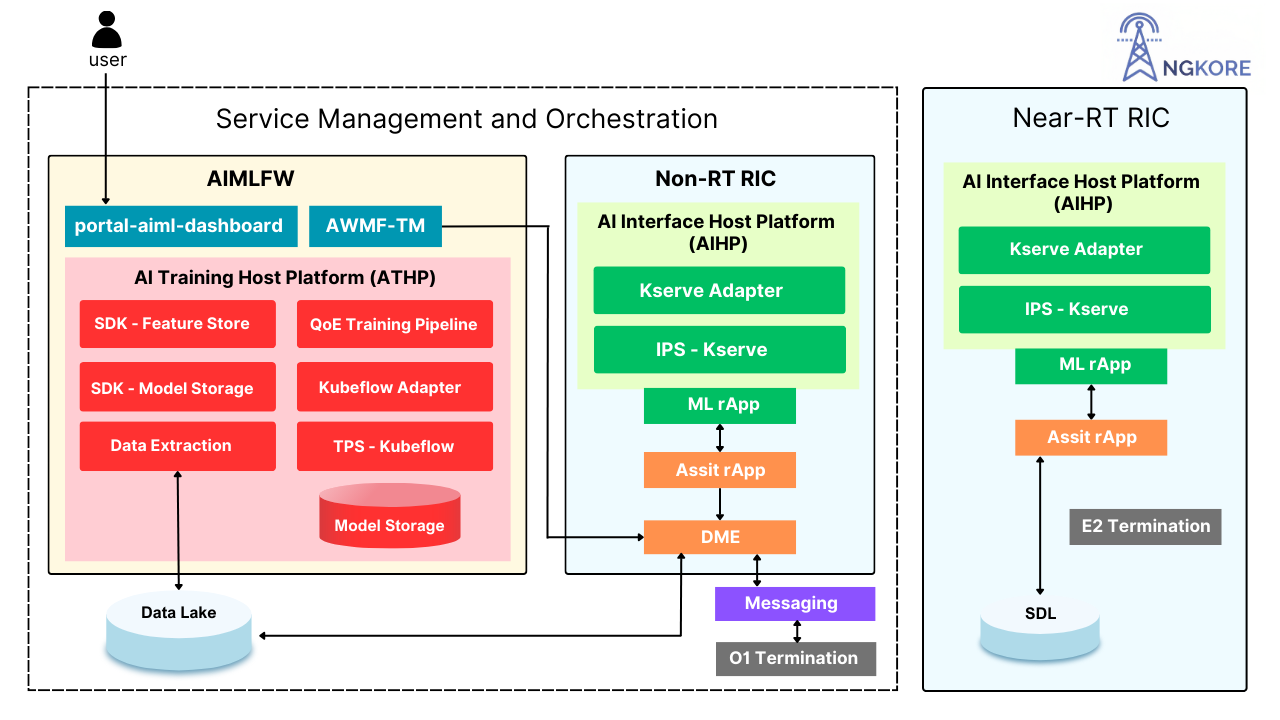
AI and Machine Learning (ML) technologies play an integral role in QoE prediction models, analyzing vast datasets to uncover patterns that impact user experience. Through continuous learning, these models become increasingly accurate, factoring in user behavior, device types, environmental conditions, and network congestion levels. In 5G, Non-Real-Time and Near-Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controllers (Non-RT and Near-RT RICs) use these predictions to make both short-term and long-term adjustments. By leveraging historical data, AI-driven models enable more informed, timely decisions, delivering a high-quality, responsive network experience that can adapt to evolving demands.
Our Near-RT RIC and Non-RT RIC are used as a host when we utilize AI/ML for prediction. You can refer to our video below showcasing the end to end deployment of AI/ML Framework over distributed RAN architecture and further applying prediction models over it:
QoE Prediction for Smart Cities and IoT¶
In smart city applications, where IoT devices are widely deployed, QoE prediction models help manage data quality and transmission efficiency. Predictive models allow cities to optimize connectivity for devices such as traffic cameras, smart meters, and connected streetlights, maintaining high performance despite network fluctuations. In dense IoT environments, QoE predictions can inform operators of areas at risk of congestion, ensuring continuous and efficient data flow. This predictive capability is especially important for applications such as public safety and transportation, where reliable connectivity is crucial for operational success.
Use Cases of QoE Prediction Models in 5G Networks¶
The application of QoE prediction in 5G networks spans numerous use cases, each highlighting the model’s importance in delivering high-quality user experiences. Some notable use cases include:
High-Definition Video Streaming: QoE prediction ensures high video quality, reducing buffering and latency, even under high demand, enhancing user experience for streaming platforms.
Online Gaming: Predicting QoE helps prevent latency and interruptions in real-time gaming, maintaining low ping rates and fast response times for an immersive gaming experience.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: In healthcare, QoE prediction ensures stable connections for remote patient monitoring and consultations, critical for real-time diagnosis and treatment.
Autonomous Vehicles: Predicting QoE helps allocate low-latency network slices for autonomous vehicles, ensuring smooth data transmission and safe, reliable operation on the road.
Industrial Automation: In factories and warehouses, QoE prediction maintains reliable connectivity for automated machinery and robots, optimizing production efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Public Safety Networks: For emergency services, QoE prediction models provide high-priority, reliable connections, ensuring timely communication during critical situations and improving response times.
Conclusion¶
Quality of Experience (QoE) prediction models have become a key component in the 5G ecosystem, enabling networks to deliver high-quality, reliable service tailored to user expectations. By forecasting potential issues and adjusting resources in real time, QoE models not only enhance user satisfaction but also optimize network performance and resource management. As 5G continues to evolve, the role of QoE prediction models will become increasingly important, helping operators deliver responsive, adaptive networks that can meet the diverse demands of next-generation applications, from smart cities to real-time gaming. Through this proactive approach, QoE prediction models are set to play a central role in the future of telecom, shaping the network’s ability to provide seamless, satisfying user experiences across all sectors.